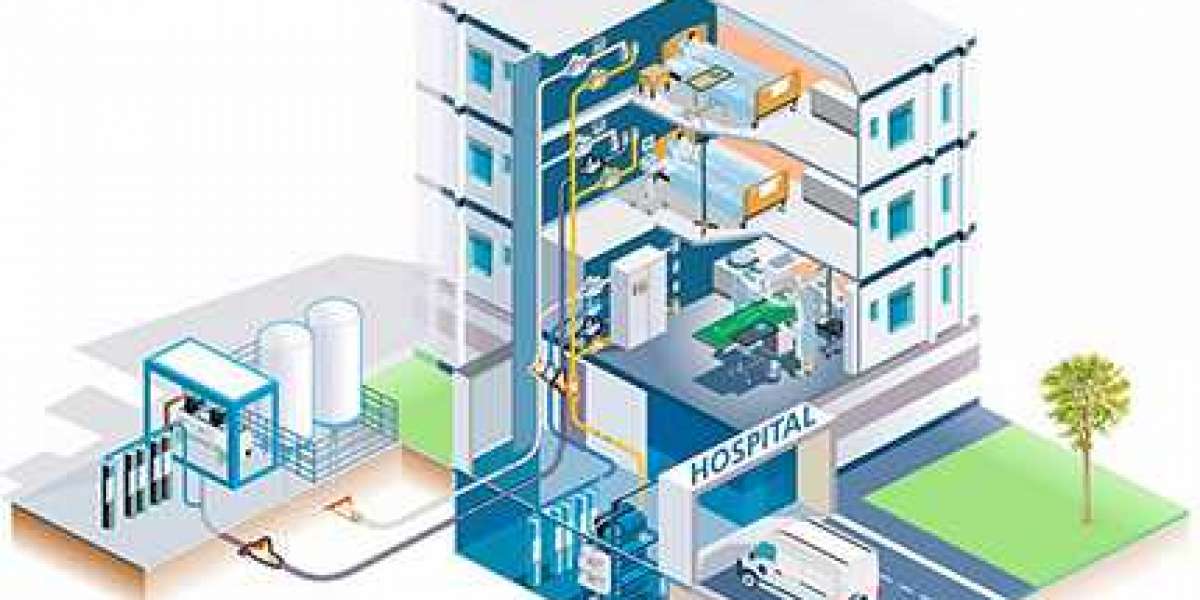
Medical gas systems work together to deliver oxygen, nitrous oxide, and waste anesthetic gas disposal (WAGD) in a healthcare facility. All the components of these systems must be carefully installed to ensure that they function properly and safely.
In addition, a monitoring system should be set up to trace the medical gas flow from the source through the piping and to the various hospital outlets that use the gases. It should also show the amount of gas remaining in different tanks and the operating condition of the supply stations.
Compressors
Medical gas systems are critical to the operation of hospitals. They supply piped oxygen, nitrous oxide, nitrogen and carbon dioxide to patient rooms, recovery areas, operating rooms, and more.
These compressors are designed and engineered under very strict standards to comply with the most extensive health regulations, so that they can provide maximum guarantees of patient safety. They also have alarm systems to detect possible faults in the gas lines and solve them in a timely manner, to prevent potential accidents.
Compressors must be dust- and mold-free, and they must be able to reliably perform to varying set pressure levels. To ensure this, they are equipped with an automatic manifold panel and a manifold reserve that engages in the event of an automatic manifold failure.
The piping from the compressor intake to the medical air receiver must be non-corrosive since it is exposed to moisture and atmospheric contaminants. It must also not be iron or galvanized, as these types of metals may oxidize and flake off under the pressure and flow of the gases. This oxidation can create fine particles that accumulate and reduce the volume of air that is delivered to the operating room.
Manifolds
Manifolds are used in medical gas systems to supply the correct pressure and volume of oxygen, carbon dioxide, nitrous oxide, and medical air from gas cylinders or tanks. The manifolds connect to the pipeline system, allowing the gas to flow uninterruptedly through the pipeline.
Medicop offers a variety of medical oxygen and nitrous oxide manifolds that supply a single gas, a combination of gases, or a single type of gas from multiple cylinders. The manifolds can be fully automatic, digital, or semi-automatic.
A fully automatic manifold automatically switches from the "Bank in Use" to the "Reserve" bank with no fluctuation in line delivery pressure. The unit also triggers an alarm when the "Reserve" bank is empty or is low.
Outlets
Outlets in medical gas systems are essential for the safe operation medical gas piping material of a facility. They enable the flow of oxygen, nitrous oxide, and other gases into various medical equipment throughout the hospital.
Typically, these outlets are located in the zone valve box. Each outlet has a hose connection for the specific gas type that it is intended to supply.
These hose connections are color coded to prevent mixing the wrong gas in an emergency, or allowing a vacuum device to be plugged into an oxygen outlet.
In addition, the hoses are protected against physical damage and corrosion and have an easy-to-clean sanitary surface.
Moreover, these outlets come in different configurations and can be used for wall or ceiling installations. They are compatible with DISS, Chemetron, Puritan Bennett, and Ohmeda connection types. They also feature an option for a satin/flat finish on the cover of the outlet.
Monitoring
SMAMEPEstimate medical gas systems deliver oxygen, nitrous oxide, nitrogen and other lifesaving gases to patient rooms and operating rooms. They must be monitored for supply level, pressure and operation condition.
Pressure sensors are an essential part of the medical gas system and help to ensure that all cylinders maintain a consistent pressure level within a range. They provide feedback to the main controller, valve or modulator.
The main benefit of pressure sensors is that they can detect leaks that could potentially contaminate the medical grade gas supply. If this happened, it could cause injury or death to the staff or patients who would be using the contaminated medical gas.
A hospital needs to hire third-party inspectors annually to ensure that all the parts of the medical gas system are functional and that they meet the required standards. Failure to pass a medical gas inspection or receiving citations can affect a hospital’s reimbursement and/or accreditation status.